Last updated on October 23rd, 2024 at 02:55 pm
Exploring the Scope of Financial Management: With Cases
Have you ever wondered how money works around the world? International Financial Management (IFM) is like a big puzzle that helps people and businesses with money from different countries. In this simple article, we’ll learn a bit more about the scope of International financial management and why it’s important for everyone, all while using easy-to-understand words.

Have you ever wondered how money moves around the globe? International Financial Management (IFM) is akin to solving a complex puzzle that facilitates individuals and businesses in handling finances across different countries. This article aims to delve deeper into the expansive scope of IFM, emphasizing its relevance and practical applications in straightforward terms.
The basic financial management definition is the wide financial activities involved in the management of financial capital.
Table of contents
Top 7 Scope of Financial Management
International Financial Management encompasses a wide array of financial activities that span borders. From managing financial resources to making crucial investment decisions, IFM plays a pivotal role in ensuring efficient utilization of funds and achieving organizational objectives. It involves strategic planning, organizing financial resources, and assessing the cost of capital to optimize financial performance. In this section I will get into the basic nature and scope of financial management.
Foreign Exchange
The scope of international financial management includes something called “foreign exchange.” Imagine you have coins from different countries, and you want to know how much they’re worth. That’s what IFM does! It helps people understand the value of money from different countries, so they know how much they need to buy things from other places.
Capital Budgeting
Another exciting part of the scope of IFM is “capital budgeting.” Have you ever had to decide how to spend your allowance? IFM helps businesses decide where to put their money, like choosing the best game to play with your allowance. They want to make sure they spend it on things that will make them more money in the future.
Risk Management
Sometimes, things can change in a country, and that might not be good for people’s money. That’s where “risk management” comes in. IFM helps people and businesses protect their money from bad things that can happen. It’s like wearing a helmet when you ride your bike to keep you safe.
Capital Markets
The scope of international financial management also includes “capital markets,” which is like a treasure map. It helps people and businesses find money to make their ideas come true. They can borrow money from others or share ownership in their business with people who want to invest.
Financing Across Borders
Imagine you have a big dream, but you need more money than you have. The scope of International financial management helps people get money from far away places to make their dreams happen. It’s like asking a friend from another town to help you.
Taxes
When you buy things, you might have to pay extra money called taxes. In the scope of International financial management, we learn how taxes work when we buy things from different countries. It’s like learning the rules of a game so you can play it well.
Objectives of Financial Management
The significance of financial management is linked to very common objectives of business. Let me discuss it step by step
- Maximising Profit
Although this might sound straightforward but its easier said then done. Especially today in the start up world, where availability of funds exists, the entrepreneurs don’t even have the perspective to think about it.
For example; In most of the ed tech startups, with investor funding at its disposal. These entrepreneurs rely heavily on marketing expenses to generate revenue or top line. However, most of them are making huge losses year on year. This goes on in the hopes of turning losses into profits.
However, the only issue is I have rarely seen any cases where this has happened. In fact, quite the opposite. Look at Byju’s, Topper, Udemy which are rarely making any money.
- Value for the promoter
The maximising of profit objective is closely related to the objective of wealth maximisation. In simple words, higher profits lead to increase in the earning per share which consequently leads to expansion of Price, which leads to Increase in value.
All of this requires diligent financial plans, including finding inefficies, improving the operating matrix’s etc.
- Liquidity Management- For Unseen Circumstances
A classic example of liquidity issues is the implementation of GST in India. The implementation of GST meant that companies had their GST credits stuck in case the vendor failed to pay the GST itself. Almost 2 lac companies in India have shut down every year since the time GST has been implemented. This is one aspect of liquidity in business. Examples of good liquidity situation are;
- Lower accounts receivable days
- High inventory turnover- leading to faster sales
- Higher credit terms with suppliers
- And finally some surplus cash
All these four aspects are in a way a sign of effective financial management.
- Consolidating Your resources
There are very few business’s that would be actually consolidating their resources on limited projects. For example; A company which is focussed on creating paints, suddenly getting into the adhesive product market is not a good sign. However, the paints company developing new verticals for industrial paints business’s is efficient use of resources.
Case studies of poor Financial Management Process
Compaq Financial Management Failure
Compaq which eventually got acquired by HP, is a classic example of poor financial management. The summarised poor asset allocation strategies included;
- Merging with DEC(digital Equipment corporation)
- The merger had no strategic objective
- The chips made by DEC were not compatible with compaq
Coca-cola’s Non Informed Decision
Coca Cola introduced the new version of their most popular drink, in order to compete with Pepsi. However, the consumers completely rejected the new version. Here is an example of poor financial decision without doing proper market research.
Importance of Financial Management
Bankruptcies
There are severe consequences of poor financial management that is already evident in my discussion in the previous section.
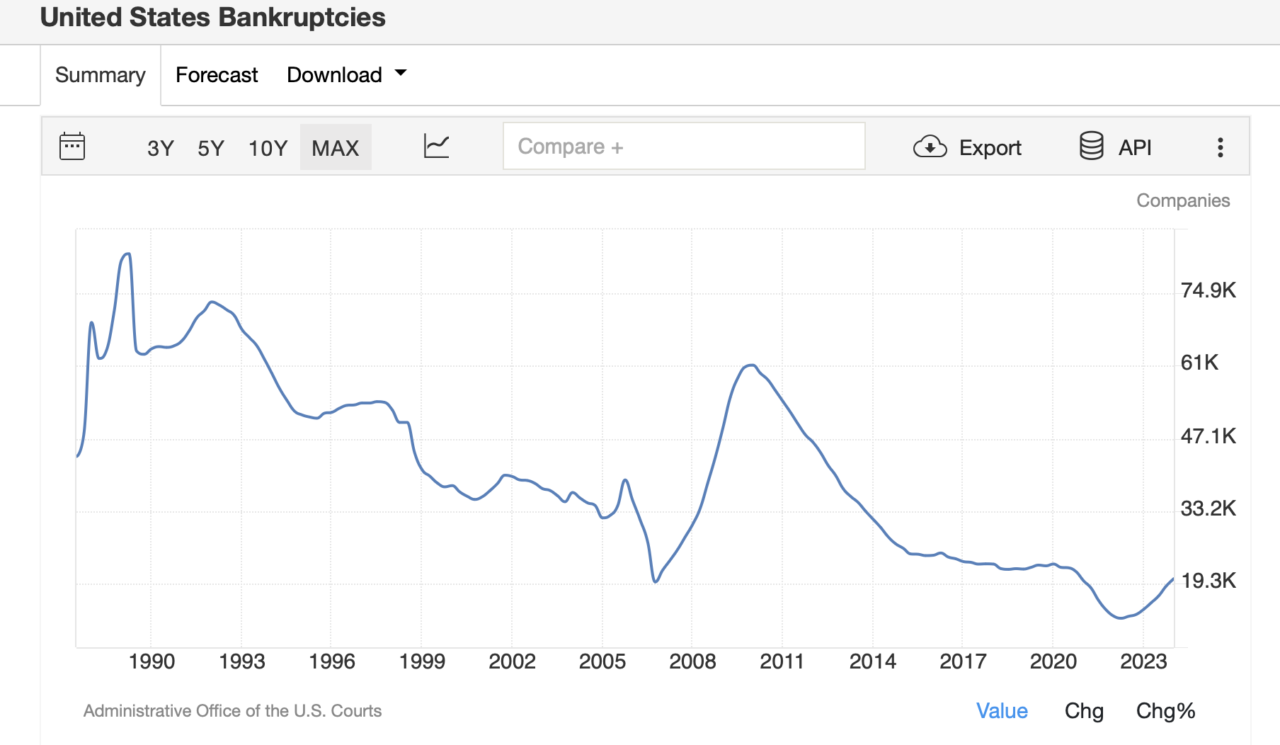
U.S Company bankruptcies on an average is around 43000, which is from the period of 1980’s to 2003. But look what happens when the business operates in euphoric times with access to easy money. In the run up to the 2008 crisis, the bankruptcies reached almost 61000.
Also interesting to note is that pre 1990’s there were more cases of bankruptcy due to another extreme, which is non availability of capital.
Now, it’s not that all these poor financial management decisions are a result of only private companies. However, there are more examples of bad financial management systems with public companies. For example with King Fisher airlines and Jet airways which went bankrupt due to bad investment opportunities.
Enhancing Financial Management with Capital Structure and Fixed Assets
Capital Structure Decisions
A crucial aspect of financial management is determining the right capital structure, which involves balancing debt and equity to minimize the cost of capital and maximize returns. Companies must carefully consider their capital structure to ensure they have adequate funds for operations and growth while maintaining financial stability.
Managing Fixed Assets
Efficient management of fixed assets, such as buildings, machinery, and equipment, is vital for long-term success. Proper maintenance and timely upgrades ensure these assets continue to contribute to the company’s productivity and profitability. Working capital management is equally important, as it ensures that a company can meet its short-term obligations and operate smoothly.
Conclusion
In essence, International Financial Management empowers individuals and businesses to make informed financial decisions on a global scale. By understanding its scope and components, one can harness the potential of international markets while mitigating financial risks. Just like mastering a new skill, learning about IFM equips us with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of global finance confidently.
FAQ’S
- Explain the scope of financial management?
Financial management’s scope has evolved over the years, with the early years in 1920’s the main focus was on liquidity management. From there the scope of financial management changed into protective covenants of outside control. In the 2000’s the prime focus was on corporate governance and transparent disclosures.
- What is Financial Management Meaning ?
Practically financial management includes activities like efficient allocation of finances, investment decisions, corporate governance. These functions might over weighted or Inder weighted based on the business’s situation.

