Last updated on January 13th, 2026 at 04:35 pm

So, you are planning to join some financial modeling course but are unsure about the correct financial modelling syllabus. Before you decide to pursue any. Firstly, it’s essential to understand the relevant financial modelling course syllabus in detail.
Many aspiring finance students and industry learners struggle because they don’t know what a complete financial modelling syllabus looks like. Most syllabus focus on a few topics but miss others that matter for real-world finance roles.
The purpose of this page is to explain what you should look for in a financial modelling syllabus especially one that covers Excel, valuation techniques, and DCF modelling comprehensively for 2025.
By the end of this guide, you will understand the key components that make a syllabus complete and practical. This will help you evaluate financial modelling courses objectively and choose programs that truly prepare you for jobs in investment banking, corporate finance, and other analytical finance roles.
What is included in financial modelling syllabus?
A complete financial modelling syllabus covers the skills and tools needed to build, analyze, and interpret financial models used in real business and finance roles. It typically includes:
Excel fundamentals: Shortcuts, formulas, model structure, and error checks
Financial statement analysis: Income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow understanding
Assumptions and forecasting: Revenue drivers, cost behavior, and growth assumptions
Three-statement financial models: Integrated projections with linked statements
Valuation techniques: DCF, comparable company analysis, and precedent transactions
Practical Examples of Financial Modeling
So let me list down a few applications of financial modelling, that I have done myself over the years.
- Helped a client with deciding on starting a sugar cane factory.
- Created a 5 year revenue forecasting for an education company
- Tested a trading strategy using back tested data
- Created numerous Equity financial models to take decision on investing
- Used it to decide a real estate purchase
- Created a marketing model for optimum spent on Facebook
So, the point I want you take away from these examples, is that its tool which simplifies any decision making. But of course dealing with numbers.
Financial Modelling Syllabus Checklist
Financial modeling is broad and if you are new to learning this then chances are you will get over whelmed. So below are my broad coverage to look out for;
Syllabus should be Comprehensive
Think of financial modelling as a tower, which needs to be built on a good deep foundation. For example; it should have a deep coverage of financial statements(accounting mechanics), Excel from modelling perspective, Template creation.
Focus on Industry Application
The use cases used in financial modelling should be easy to understood. Financial models typically can get very complicated, when you begin. There are so many moving parts, look below and you understand that a lot of things are inter connected. So the models covered in a syllabus should be simple business’s to understand.
The following sectors should be avoided as a beginner: Oil & Gas, Banking, Chemicals, Pharama. Unless of course you have some background in such sectors.
Should Start From Scratch
It takes years to master this skills, because there are two parts to it. One is skill, the other is experience of sectors and business’s. While you might be great with the skill (Like template creation etc) but you need to spend business’s cycles with sectors to truly understand.
Nevertheless, below four outcomes should be targeted
- Understanding the linkages of income statement, balance sheet and cash flow statement.
- Have an understanding of how various business’s decisions and their financial impacts.
- Gain some insights how and to what extent can a financial plan predict future.
- Also gain understanding of the limitations of financial modelling and valuation.
Should Cover Business Research
There are four major components of financial modeling which are assumptions, financial statement analysis, valuation and sensitivity analysis. ;
- Assumptions are the most important since they are in the form of forecast of the future of the company.
- Financial statement analysis focuses on the ability of the firm to perform
- Valuation estimates the value of the firm in the market.
- Scenarios to gauge how they affect the model and its accuracy and reliability
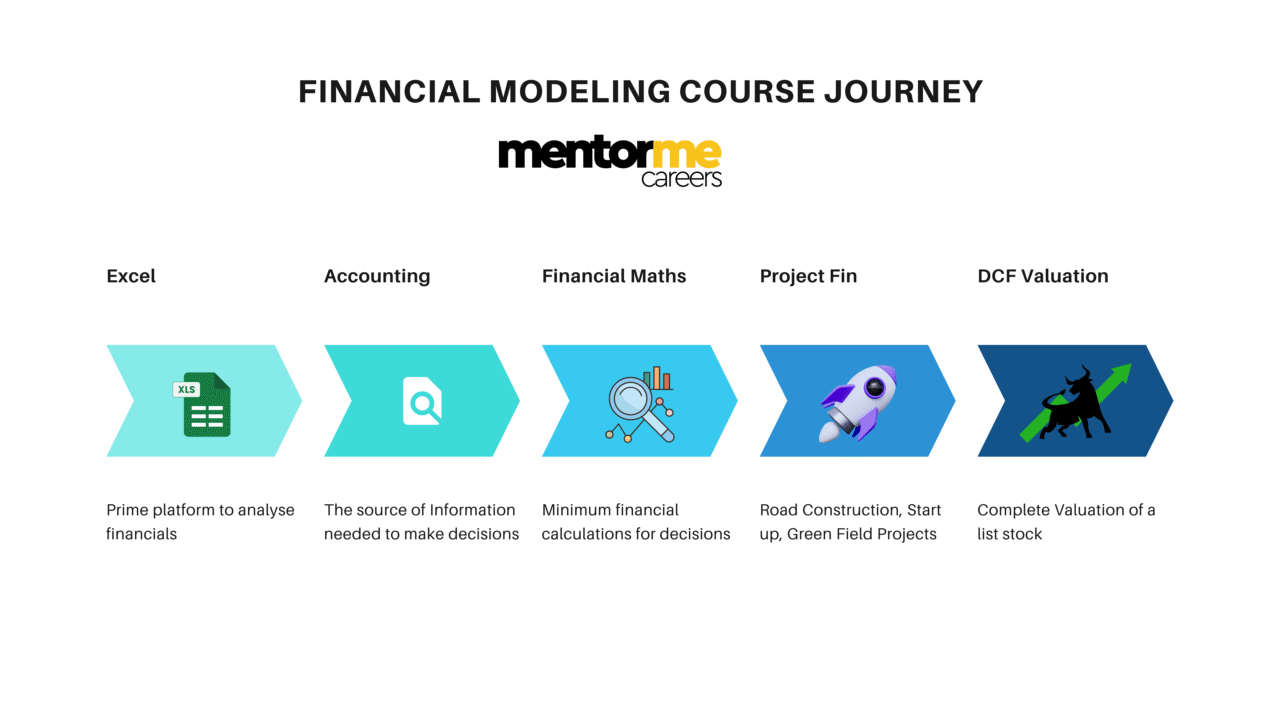
Course Modules in Financial Modelling Syllabus
With my own experience of using financial modelling skills and also teaching financial modelling to various types of students. Below is my recommended coverage;
Here’s a table outlining the weightage of these topics in a financial modeling syllabus for a beginner:
- The weightage which I have mentioned above is ideal especially for beginners trying to learn this skill.
Financial Modelling Detailed Syllabus
Here’s a well-formatted syllabus for a financial modeling course which covers all the aspects of the minimum checklist I shared at the start.
Financial Modelling Syllabus – Detailed
- Spreadsheets, cell referencing, freeze panes
- Lookups (VLOOKUP, HLOOKUP, INDEX, MATCH)
- Logical operators, SUMIF, Pivot tables, Slicers, Dashboards
- Assignments: TVM basic & advanced, sensitivity analysis
- TVM, IRR, XIRR, MIRR, NPV
- Discount rate, SIP selection, portfolio allocation
- Central tendency, histograms, dispersion measures
- Beta, covariance, drawdown, risk modeling (NIFTY, Crude, Gold)
- Accrual concept, linking financial statements
- Financial statement creation in Excel
- Concept, challenges, and group project
- Income, balance sheet, cash flow statements
- FSA quiz and employability evaluation
- Activity, solvency, leverage ratios
- Case studies: Asian Paints, Berger Paints
- Setup costs, IS-BS-CF linkage, scenario analysis
- Construction phasing, moratorium, returns calculation
- MAT, MAT credit, IRR impact, DTA/DTL modeling
- Revenue, costs, construction, asset/debt schedule, taxation
- CAPM, Gordon Growth, WACC, Terminal Value
- Identify required data, analyze annual reports
- Financial statement structuring with real data
- Price × Quantity model, forecasting methodology
- Debt, asset, depreciation schedules, final valuation
- Present investment thesis using storytelling format
- Road Project Finance Modeling (8 Hrs)
- Port Finance Modeling (6 Hrs)
- Real Estate Modeling (6 Hrs)
- IT Public Listed Modeling (8 Hrs)
- M&A Modeling (4 Hrs)
- LBO Modeling (4 Hrs)
- Excel VBA for Finance (4 Hrs)
- Aviation Business Modeling (12 Hrs)
- Start-up Business Modeling (12 Hrs)
- Advanced Excel Formulas (4 Hrs)
- Algo Trading Modeling (30 Hrs)
Tools You Will Learn
Now, as soon as someone says tools the tendency is to think that they have to be some softwares like excel and power BI. However the definition of tools in financial modeling are basically the academic theories which need to be learned to use it in financial modeling.
- Financial statement Analysis- Its a tool to understand the reliability of a companies operations
- Excel – Is a tool to put all the information in a platform to analyse further
- Quants- to calculate present value, future value, valuation etc
- Power BI- to finally present our findings in a very visual and engaging manner
- Python- which helps in dealing with creating statistical conclusions, when the data is large
Types of Financial Models Covered in a Syllabus
A comprehensive financial modelling syllabus includes the most widely used models applied across finance and investment roles. Common models covered are:
- Three-statement financial model: Integrates income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow projections.
- Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) model: Estimates intrinsic company value using projected cash flows.
- M&A model: Analyzes the financial impact of mergers and acquisitions.
- LBO model: Evaluates leveraged buyout feasibility and investor returns.
- Comparable company analysis (Comps): Values businesses using market multiples of peer companies.
These models form the core practical foundation of a strong financial modelling syllabus.
Financial Modelling Syllabus Recommender- Based on Background
Find which topic you need to focus on.
Click here to get started
High
Medium
Low
High
Medium
Low
High
Medium
Low
High
Medium
Low
High
Medium
Low
What Jobs Require Financial Modelling Skills?
Financial modelling skills are required in roles where decision-making depends on forecasting, valuation, and financial analysis. Common jobs include:
- Investment banking roles for deal analysis, valuation, and client advisory
- Corporate finance roles for budgeting, forecasting, and strategic planning
- Equity research roles for company analysis and investment recommendations
- Private equity and venture capital roles for evaluating investments and portfolio performance
- Financial analyst roles across industries for performance analysis and reporting
- Management consulting roles for modeling business scenarios and strategic outcomes
These roles rely on financial modelling to turn data into clear, actionable insights.
FAQ’s Financial Modelling Course Syllabus
A typical financial modelling course syllabus curated for a beginner should include, excel , financial statement analysis, project finance, financial mathematics and equity valuation.
As I have mentioned earlier that advance topics include mergers and acquisition modeling, Leveraged buyout modeling, real estate valuation.
So, the non negotiable four components of financial modelling syallbus are; project finance, financial statement analysis, excel and equity valuation
Since financial modelling is a decision making tool used in finance, the major things taught are excel, financial statement analysis, equity valuation and project finance
Majorly the software used is excel for core modeling but for presentation tools and software like Power BI can be used
Related to Financial Modelling Syllabus


