Last updated on June 29th, 2024 at 02:05 pm
Bullish meaning in the capital market is a term denoting the sentiment of people about the capital markets in general. Bullish means that people have a positive sentiment of the stock market and expect the price to go up. Whereas, bearish meaning that the sentiment is negative, expecting the price to go down.
‘Market crash ho gayaa’ (Translation: The market has crashed) is a term that strikes fear in the minds of every investor. When you turn on the news channel, all you can see are terms like the market, economy, bull market, bear market, etc. So, what exactly is a Bull and Bear Market. I will be explaining what these markets are, their characteristics and what one should do in each of the market scenarios.
Bullish and bearish meaning
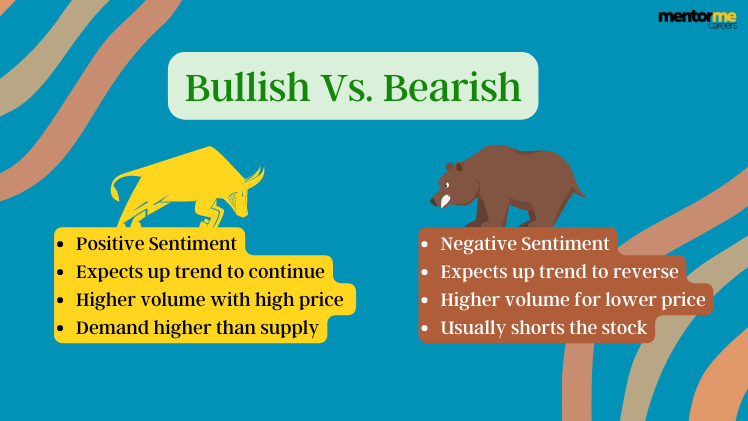
When it comes to the investing world, the terms ‘bull’ and ‘bear’ are often used to determine the market conditions based on whether the price movement is positive or negative. When analysts use the term ‘bullish market’ and ‘bearish market’, they are describing whether the market is being optimistic (likely to rise) or pessimistic (likely to fall). Both these terms are a sentiment or mindset adopted by a trader. Bullish sentiment is where they think the price of the securities will go up and bearish sentiment is where they think the price of the securities will go down.
The terms bull and bear are derived from the way in which each animal attacks its opponents [1]. Whenever a bull attacks, he will thrust its horns up into the air. Hence, any positive movement in the market is referred to as a bullish market. Whenever a bear attacks, he will swipe down with his paw to hit his opponent. Hence, any negative movement in the market is referred to as the bearish market.
Causes of Bullish and Bear Market Trends
Now, its important to understand bullish and bearish meaning with the help of underlying causes.
Supply and Demand
In a bullish market, there is a strong demand low supply of securities. This means that many investors are looking to buy securities but not a lot are willing to sell them. This results in an increase in the price. The investor should try and enter the bullish market at an early trend and sell when the securities reach their peak. In the bear market, it is completely the opposite. In a bearish market, the demand is very low, but the supply is strong. So, not a lot of people are willing to buy but there are many investors who are willing to sell. This leads to a decrease in the prices of securities [2]. The investors can profit from Short Selling, putting options, or choosing safer investments such as fixed deposits.
Change in Economic Activities
The stock market and the economy are strongly linked together. In a bullish market, the earnings increase, and the economy grows as people are willing to buy goods and services more often. This leads to more wealth and growth of the economy. On the opposite hand, in a bearish market, consumers set stricter policies and reduce their spending which leads to lower sales and a fall in business profits. This consequently results in falling of the prices and a negative impact on the GDP
Investors Psychology
Market behaviour is impacted by how individuals perceive and react to the market’s performance. It is the psychology of the investor which determines whether the market will rise or fall. This means that the stock market performance in the psychology of the investor is mutually dependent. Hence investors more willingly participate in a bullish market in the hope of obtaining a profit.
In the case of a bearish market, the market sentiment and the investor’s psychology are negative. Investors begin to move their money out of the equities into fixed-income securities. The decline in the market performance shakes the confidence of the investor. This causes the investor to keep their money out of the market, which consequently results in causing a general price decline as outflow increases.
Impact of Interest Rates on Financial Markets
Interest rates play a pivotal role in shaping financial markets. In a bullish market, lower interest rates can stimulate borrowing and investing, further driving up stock prices. Conversely, in a bearish market, higher interest rates can dampen economic activity and lower stock prices. Monitoring interest rate changes is crucial for investors to make informed decisions about their asset classes.
Historical Perspectives ON bullish and bearish meaning: The Great Depression to the Longest Bull Market
The Great Depression was a significant bearish period that saw a dramatic decline in the Dow Jones Industrial Average. In contrast, the recent period from 2013 to 2019 marked the longest bull market in history, particularly in the S&P 500. These historical events provide valuable insights into market dynamics and investor behavior, highlighting the importance of understanding both short-term fluctuations and long-term trends.
Strategies for Bullish and Bearish Market
As previously mentioned, you can make a profit in both bullish and bearish markets. Let us look at how this is possible. During a bullish market, the investor should take advantage of the rising prices of securities by buying stocks early at the start of the trend, if possible. They can then sell them when they have reached their peak. One should note that perfect timings in the market are almost impossible. During the bull run, the investor should make sure that his losses are minor and temporary.
In the bearish market, the chances of losses are significantly higher because the prices are continuously falling. Even if you invest with the hope of an upside, you are more likely to face a loss. In such scenarios, one should turn toward Short Selling, or think about safer investments such as fixed-income securities i.e., FDs. The investor can also turn to the stocks whose performance is not affected much by the decline in the economy. Such type of defensive securities is beneficial in both glooming and booming cycles of the economy. A few examples of such defensive stocks would be utilities that are owned by the government, FMCG (Fast Moving Consumer Goods), etc. These are a few necessities that consumers buy irrespective of the economic conditions.
Bullish Market Time Line of India
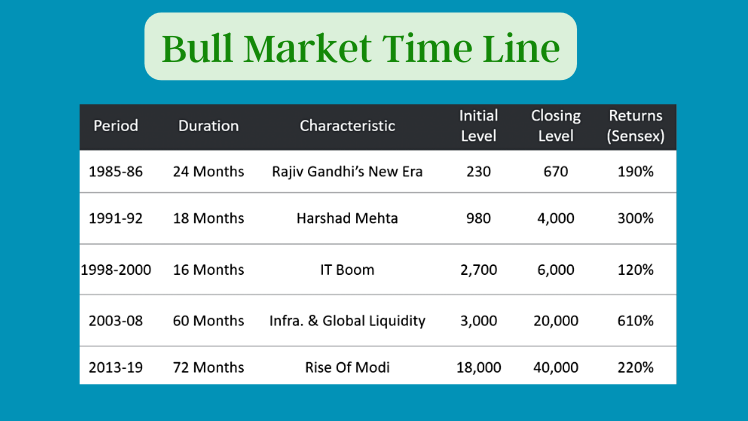 Bull market history of India
Bull market history of India
- So India currently, between 2013-2019 is the longest-running bull market of 72 months with a total increase in sensex of 220%
- Second to the rise of mode is the global run and the global crash between 2003 and 2008, which lasted for around 60 months.
- Third, is the rajiv gandhi era, where the market were in bull run for almost 2 years with a increase in sensex by 190%.
- Finally, in terms of returns the Harshad mehta scam period is the mother of all bull runs with a return of 300%.
Conclusion
Both bullish and bearish markets significantly impact investments. Understanding market direction and making informed investment decisions is crucial. The stock market has historically recovered from crashes, emphasizing the importance of long-term perspective.

