Last updated on October 23rd, 2024 at 03:57 pm
What is Net Book Value?
Net Book Value, also known as the net asset value, is the value at which the company reports its assets on their balance sheet. It is calculated by netting against its accumulated depreciation. This is how many companies also calculate their NAV (net asset value). It is calculated as total assets- minus intangible assets and liabilities. The Net Book Value is calculated using the asset’s original cost and the depreciation and amortization are subtracted from it. The book value of any company is often lower than the company’s market value. Book Value plays a very crucial role in fundamental analysis.
Calculating Net Book Value
The formula for calculating the Net Book Value is as follows:
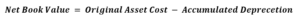
Where:
- Accumulated Depreciation = Depreciation per year × Total Number of Years
Let’s look at an example. A logging company purchases a truck for $200,000 and the truck depreciated $15,000 per year for 4 years. The NBV would be calculated in the following way:
Accumulated Depreciation = $15,000 × 4 years = $60,000
Net Book Value = $200,000 – $60,000 = $140,000
So, the NBV of the logging companies after 4 years would be $140,000.
Importance of Net Book Value
Book value is one of the most crucial and important aspects when it comes to financial analysis. It is important for the valuation of the company when and if the company is considering liquidation or a merger with another company. The Net Book Value and market value are typically not equal. Market value depends on supply and demand for the asset. The depreciation is always accumulated every year. The NBV is affected by this as it is netted against the accumulated depreciation. It makes fair and accurate accounting records and helps express a true approximation of the company’s value.
Since the company’s book value represents the shareholding worth, comparing the market value of the shares can serve as an effective technique while deciding the share price. By using the book value, one can determine if any share is underpriced, overpriced or at par. Book value has two main uses:
- Serves as a total value of the company’s assets that the shareholders receive if the company liquidates.
- Valuation in the share price of the stock.
Book value per share (BVPS) is a method of calculating the per-share book value of a company based on common shareholders’ equity in the company. If the company dissolves, the book value per common share indicates the price value remaining for common shareholders after all assets are liquidated and all debtors are paid. If a company’s BVPS is higher than its market value per share, then its stock may be considered to be undervalued.
Book Value Formula and Its Components
The book value formula is a straightforward calculation used to determine the value of a company’s assets minus its liabilities, as recorded on the balance sheet. This formula plays a vital role in understanding a company’s financial status. The company’s book value can differ significantly from the company’s market value, reflecting the difference between the recorded asset total and the market perception of value. This discrepancy often influences stock prices and investor decisions. For instance, if a company’s stock market value is lower than its book value, it might indicate that the stock is undervalued, presenting a potential investment opportunity.
BVPS and Its Relevance
Book Value Per Share (BVPS) is a key metric derived from the company’s book value, calculated by dividing the book value by the number of shares outstanding. BVPS provides insight into the per-share value of the company based on common shareholders’ equity. It is especially useful when assessing the worth of a company’s stock. If the BVPS is higher than the market value per share, the stock may be considered undervalued. This metric is crucial for making investment decisions and understanding the financial health of a company. The BVPS formula is:
BVPS=Book ValueTotal Number of Outstanding Shares\text{BVPS} = \frac{\text{Book Value}}{\text{Total Number of Outstanding Shares}}BVPS=Total Number of Outstanding SharesBook Value
Application of Net Book Value in Financial Analysis
The application of net book value extends to various aspects of financial analysis. Companies often use this value to evaluate the worth of their tangible and intangible assets such as patents and other intellectual property. These valuations play a crucial role in determining the overall health and potential growth of a company. Understanding the net book value helps in making informed investment decisions and assessing the impact of depreciation and amortization on long-term assets. Furthermore, the net book value provides a clearer picture of a company’s financial position when compared to its market value, aiding in comprehensive financial analysis.
Conclusion
Net Book Value is a fundamental concept in accounting and finance, offering a reliable measure of a company’s asset value after accounting for depreciation. It is crucial for financial analysis, especially when evaluating a company’s worth during liquidation or mergers. By understanding the book value formula and its implications, investors and stakeholders can make more informed decisions regarding their investments and the financial health of a company.

