Last updated on February 8th, 2024 at 02:03 pm
In disguised unemployment, everyone appears to be working, but there isn’t enough full-time work for everyone. Seasonal unemployment refers to the phenomenon of certain industries experiencing a spike in joblessness at specific times of the year.
Seasonal unemployment, on the other hand, is a type of unemployment in which people cannot find work during specific months of the year.
In this blog, we are going to learn about what is the difference between disguised unemployment and seasonal unemployment.
| Disguised Unemployment | Seasonal Unemployment |
| People are employed, but no output | People are employed only for specific Months |
| MNREGA Schemes in India are a close example | Life Guards who are not required during winters |
| Mainly found in agriculture | It is it agriculture and other industries too |
| Used by governments for job security schemes | Is an outcome of industry features |
What is the definition of Seasonal unemployment?
Unemployment is defined as a period in which an individual cannot work.
To put it simply, you might be physically and mentally fit to work, but you can’t find work based on your level. Hence It is, in essence, a state of automatic worklessness or idleness.
On the other hand, Unemployed people are not able to find a job, not because skill versus compensation match.
Unemployment can be divided into two categories: rural areas unemployment and urban unemployment. Open unemployment, seasonal unemployment, and disguised unemployment are the three types of rural unemployment.
Also Urban unemployment, on the other hand, is divided into three categories: industrial unemployment, educated unemployment, and technological unemployment.
What Is the Meaning of Disguised Unemployment?

When a portion of the labor force is either unemployed or not working at full capacity, worker productivity is essentially zero; this is known as disguised unemployment. Unemployment rate is the only factor that has no bearing on overall output. When productivity is low, and there are too many workers filling too few jobs, the economy exhibits this kind of unemployment.
Example: MNREGA, which is debatable whether it has worked or not. As per various news articles, it’s unclear what asset was created with this disguised employment.
Important takeaways
- Unemployment isn’t affecting overall economic output.
- When productivity is too low, and there are too many workers filling too few jobs, this happens.
- It can refer to any large population segment that isn’t working to its full potential.
The various types of Disguised Unemployment
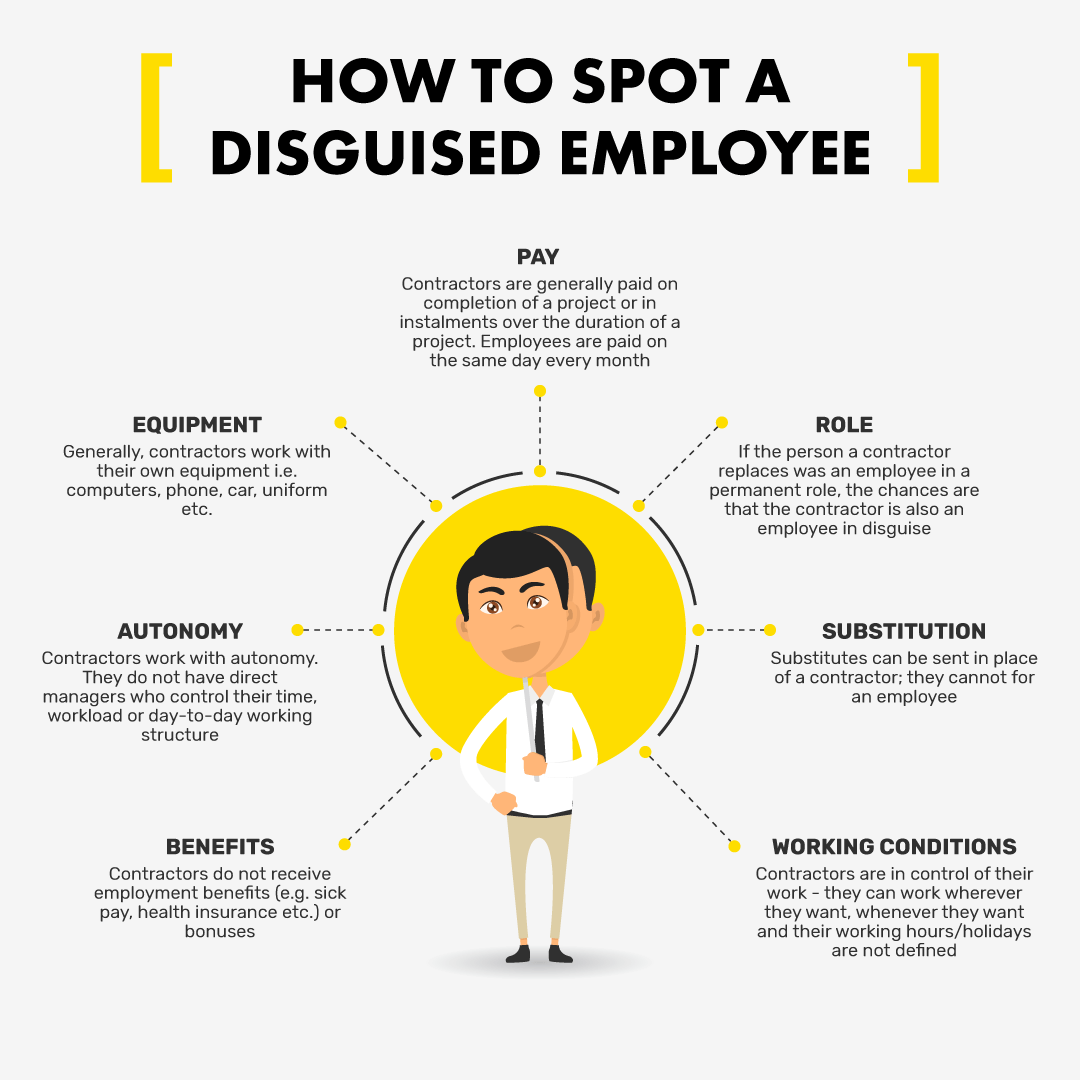
So let’s use the following image in helping in understanding disguised unemployment.
Underemployment
People who work part-time but want and are capable of doing full-time work may be considered disguised unemployed in certain circumstances. It also includes people who accept jobs that are well below their skill level. In these cases, disguised unemployment is also known as “underemployment,”. This refers to people who are working but not to their full potential.
A person with a master’s degree in business administration (MBA) who accepts a full-time cashier position because they are unable to find work in their field may be considered underemployed. This is because they are working below their skill set. A person who works part-time in their field but wants to work full-time may also be considered underemployed.
Illness and Impairment
Those who are sick or are considered partially disabled may also be included. Even if they are not actively working, they may be able to contribute to the economy. When someone is receiving disability benefits, this type is temporary in the case of illness. As a result, the individual is frequently excluded from national unemployment statistics.
No Longer Looking for Work
When a person stops looking for work for any reason, they are often no longer considered unemployed when the unemployment rate is calculated. To be counted as unemployed in many countries, a person must be actively looking for work. If a person stops looking for work, whether for a short or long period of time, they are no longer counted until they resume looking for work.
What is the definition of a seasonal job?
Seasonal employment is one that is only available at certain times of the year. During the holidays, many seasonal opportunities become available. These themed attractions and events open and require workers. Seasonal jobs are also available, such as in agriculture or tourism, and are tied to the weather. Customer service, sales, performing, and manual work are examples of these vocations. While many seasonal jobs only offer part-time work, you can also discover full-time, seasonal jobs. Here are a few seasonal work examples:
- Theme park employee
- Seasonal event staff
- Seasonal sales associate
- Holiday performer
- Lifeguard
What is seasonal unemployment?
Working a seasonal job can provide fascinating possibilities. They provide opportunities to work in unique environments and execute tasks that are distinctive to a certain season. Seasonal occupations are often only available for a portion of the year. People who work solely in seasonal jobs may find themselves unemployed after the season ends. Knowing how seasonal unemployment works might help you prepare for the duration of a seasonal job and make plans for what to do when the opportunity ends. We define seasonal unemployment and look at how it works in this post.
When the demand for labour falls, those who work in seasonal jobs become unemployed. This normally happens when a season finishes and a new one begins. This happens when a holiday or because of weather changes. Someone who works in a resort during the summer, for example, may find themselves unemployed when the fall arrives and the summer facilities must close.
Seasonal unemployment is common in tourist-heavy areas. It happens as different tourist attractions increase or decrease operations depending on the time of year and season. This is especially true for outdoor tourist attractions, which may only be able to operate in certain weather conditions.
How to avoid disguised employment?
In circumstances of possible disguised employment, each country has its unique assessment procedures. As previously stated, having a contract that specifically identifies the relationship as a contractor does not guarantee that the classification will be accepted by a ruling judge. In the event of an audit, however, drafting a contract that clearly defines the connection is critical. Furthermore, in the event of a dispute, a good contract that is legally binding and localized for both countries involved will shield you from the possibility of re-qualification.
Here are some of the characteristics of a good contract:
- The amount of money paid for the work done The resources made available by the parties
- The mission’s or service’s duration, as well as renewal, notification, termination, and dispute clauses
- The parties’ signatures and the date
- The parties’ identities are established (the service provider and the client)
- The nature of the service to be given clearly and completely specified
- The parties’ specific responsibilities
Although drafting a strong contract may appear to be a difficult undertaking. It is critical to devote time and effort to it. Before beginning the assignment, come to an agreement on your conditions. If you’re a contractor and your working conditions are starting to resemble those of a full-time employee, talk to your client about finding common ground and reducing hazards.
Governments’ Approaches to Seasonal Employment
Aside from that, the informal sector in every country, especially developed ones, sees seasonal employment since the occupations in the informal sector are such that they cannot be sustained year-round.
As a result, it is customary for governments and other stakeholders to assume responsibility. It’s for assisting farmers, farmhands, and workers in these sectors with monetary and nonmonetary help so that they have a source of income during periods when they are unemployed.
The Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act, implemented by the Indian government, is a famous example of this. It requires whichever government is in power to give work to the rural labor during the offseason months.
Furthermore, various programs give jobs during the months when construction and manufacturing industries are unemployed. It’s worth noting that most governments throughout the world intervene when seasonal employment leaves workers unemployed.
Why is it so difficult to solve the problem of seasonal employment?
What makes the problem of seasonal employment more difficult to solve are two issues. One is that the structural nature of such industries makes year-round employment unfeasible. And two, workers in the unorganized and informal sectors frequently operate outside of the formal pension and social security systems. They cannot be tracked or provided with concrete assistance.
This is why the Indian government has insisted on Aadhar identification. It is used as a method of enumerating the informal and unorganized sector workforce in order to ensure that they receive the benefits that they are entitled to.
However, many critics of the handout for seasonally employed people point out that such workers can find work that is similar in nature and available throughout the year.
In other words, they argue that employees with basic skills can find jobs that are non-specialized and routine if they try hard enough. Such critique is typical among conservatives who are opposed to any type of government help to employees in the first place.
How to solve the problem of disguised employment?
There a large-scale minority in the agriculturalist sector in underdeveloped countries. There is also a large-scale minority in the urban areas. In agriculture, underemployment dens and disguised huts are open and evident, whereas, in the city, they are hidden. Now the debate is whether it should be supplied to individuals who are completely employed or to those who are somewhat working or unemployed.
There isn’t much room for saving potential in agriculture for capital formation. The greatest option is to establish jobs in urban areas for individuals who are unemployed. The prudent course appears to be to first employ the completely unemployed and then address this problem

What is the best way to eliminate unemployment?
The best way to eliminate hidden unemployment, in our opinion, is to increase agricultural productivity through agricultural advances. Agricultural productivity can be increased by using modern agricultural inputs such as high-yielding seed varieties, high-dose fertilizers, insecticides, and adequate irrigation. Then there will be new agricultural job prospects available. A multiple-cropping system, for example. It necessitates additional labour. If this technique is widely adopted, employment will most likely rise, and unemployment will fall.
By increasing agricultural productivity or developing agriculture, the problem of underemployment can be overcome.
Because some workers in this scenario do not have enough work to do, and their departure will have no effect on output, their marginal productivity is zero. However, if there is a green revolution, agricultural output will increase, and more and new job opportunities will become accessible. The issue of hidden unemployment will be addressed.
We can see that it is not required to remove workers from agriculture whose marginal production is 0 in order to eliminate disguised employment. However, by improving agricultural methods, we can increase their marginal productivity in that area. This would solve their problem, and there would be no difficulty in removing the disgustedly unemployed labor and placing them in productive employment elsewhere.
Important distinctions about what is the difference between disguised unemployment and seasonal unemployment
Following our discussion of the definitions of the two types of unemployment, we will now look at the differences between disguised unemployment and seasonal unemployment:
- Disguised form occurs when the overall number of workers performing the work or job is much larger than the real number of workers required. Seasonal unemployment, on the other hand, occurs when there is a shortage of productive work during a given time of year.
- Disguised When a section of the workforce becomes redundant, unemployment develops. Seasonal unemployment, on the other hand, results in lower demand for labor than normal during peak months.
- Disguised form is most prevalent in agriculture. It’s where even if only two people are needed to cultivate the farm, five people are employed. Seasonal unemployment, on the other hand, is most common in agro-based industries. It is where a large workforce is required during peak seasons, and no such labor is necessary during lean months. As a result, work is only available during certain seasons or for a limited period of time.
- While seasonal unemployment contributes value to production whenever possible. In the sense that value is added during the months of demand. Disguised form of problem adds no value to production, in the sense that even if some workers are withdrawn, the productivity level will remain the same.
Conclusion
Unemployment causes a waste of the country's human resources, turning assets into liabilities for the economy. It adds to the economic overburden. When an individual does not contribute anything to the total output, is that makes this kind of unemployment more distinct." On the other hand, seasonal unemployment occurs throughout a specific period of the year. We hope you have got a basic idea regarding what is the difference between disguised unemployment and seasonal unemployment.