Departmental accounting in a nutshell is basically breaking down of the entire organisation into smaller branches. While creating an individual Profit and loss account for each of them. The question to ask in terms of this topic, Is why would you use this method? In this article I will take you through the bits and pieces of it in detail with examples and case studies.
Key Takeaways
- Departmental accounting is a process of segregating the business into smaller divisions and creating their own financial statements.
- Cost is allocated based on some basis like time allocated, floor occupied etc
- Departmental accounting is different compared to branch accounting.
- It helps in improving the efficiency of budget allocation and decision making.
Meaning of Departmental Accounting
I will explain what departmental accounting means with an example. Imagine we have a book store and want to separate it into different sections. So how would we do it?
- Firstly you could start with book types- Like fiction, non fiction, children books
- Secondly, you could also start with location or geography of the various stores.
Hence, what you should understand is that this method of departmental accounting works of the principle of finding clusters. While the clusters itself depends on the objective.
Objectives of Departmental Accounting
So, now let me briefly touch upon the major objectives of departmental accounting;
- First, it helps in comparison of one particular line of business with another.
- Second, it helps the business owner in deciding which business line should he invest in or expand.
- Third, it can help also the management to decide the rewards for each of the departmental owners.
- Finally, it helps in budget allocation across the clusters.
Types of Departments
Before I dive into the specifics, its important that you know that there are basically two types of division.
- Independent Departments
These are departments which work alone and have no dependency of costs and price with others. Examples include Human Resource, or sales.
- Dependent Departments
The opposite of independence, like the operations and logistics department which of course would be dependent on manufacturing.
Features & Types of Departmental Accounting
Now, let me take you through the various features of departmental accounting and also briefly discuss the features.
Bifurcation of Books
First, the first feature is that each department would have its own set of books. Which is easy to say but needs a lot of processes to control. However think about it, would it possible to implement this in a small business? The answer is no, because of the costs and complication associated with it.
Big companies like TATA, HUL, Titan actually use such methods.
Combined Method
I hope you noticed the challenge with this method for collating results of each department, profit of each department. Which of course helps you to compare the performance more minutely. However, a small business department manager would have a hard time implementing this in the final accounts.
Hence there is also a combined method, which basically does not create individual balance sheet for each accounting period. But instead of creating different books, we instead create separate columns.
Advantages of Departmental Accounting
So, obviously if you are able to execute this properly, then it will definitely give a lot of advantages. However, still lets discuss some of the main benefits below.
- It helps in cross department comparison
- Facilitates logical and precise compensation plans
- Provides a foundation of budgets
- Improvement of performance minutely across divisions
- Builds more internal control over each business line.
Expense Allocation Basis
In this section I shall discuss the, allocation of expenses in departmental accounts. For example; if the company provides canteen services to all employees versus lets say stationary costs. These two type of expenses are either common or individual. However that is just an example to make you understand the context.
- You can categorize rent expenses by division according to the size and space utilized.
- Depreciation cost is divided based on total assets used by the division.
- Energy costs can be easily calculated for each area if they are in separate divisions or spaces.
- Costs for senior management, such as MDs and directors, can be split based on the time they spend in each division. This allows for expenses to be assigned according to where they dedicate their time.
- If a director spends more time in one division, the expenses for that division will show this difference.
Illustrations 1: Transfer Price
Let me start with an example;
There is a fiction book division of a publisher. Which transfers books at 50% plus of the original cost to the non fiction division. While the closing stock of the the non fiction division is $27000. What would be the stock reserve?
So let us take this step by step;
- First the fiction department transfers the books at $27000, which includes a 50% profit. Hence if we consider that the price per unit was $100 and Profit was $50 then the transfer price is $150.
- You can calculate the profit that needs to be attributed as $50/$150 X $27000 = $9000.
So the stock reserve will be $9000.
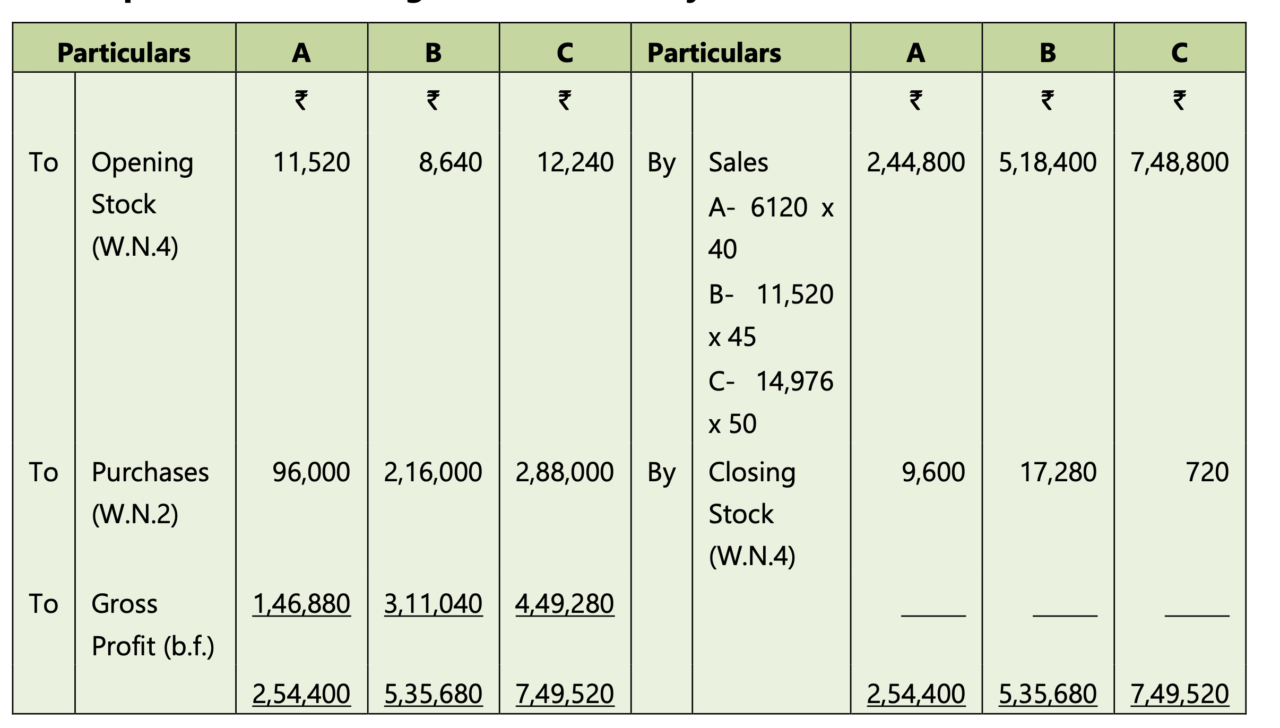
Illustration 2: Departmental trading and profit and loss account
Consider the following information of various departments and prepare a departmental trading and profit and loss account.
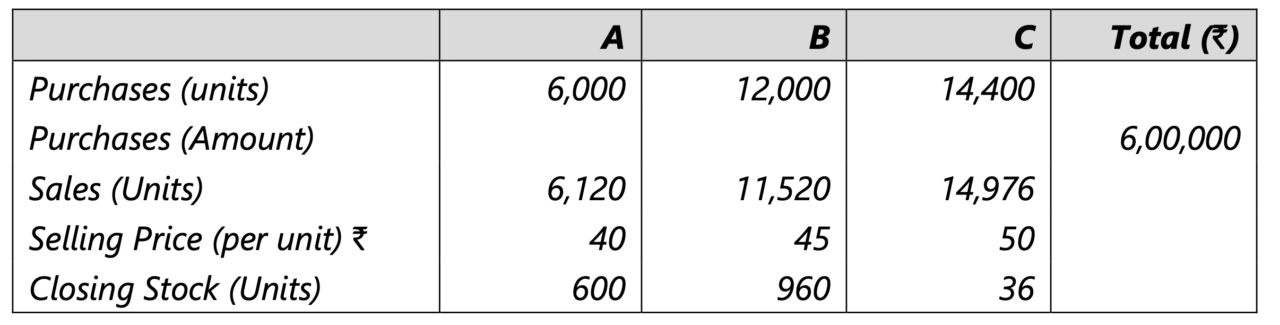
The solution is given below
Departmental Accounting vs Branch Accounting
There can be a little confusion between these two types of accounting, because the difference is a thin line.
- For this you need to understand that a department is the part of the same organisation under the same roof. However a branch is not the part of the main organisation
- For example; if you look at the jewellery division in Titan company. It is a branch not a department of TITAN. While it was carved out because this business line expanded.
- The marketing team at TITAN’s jewellery division is part of the parent company’s jewellery business.
- Another difference is that departments are never classified geographically compared to branches which are.
Conclusion
I hope the basic difference between and understanding of departmental structure and branch structure is clear now. This was a very generic discussion on the basics of this concept, however it’s a good base to start with for this concept.
While intuitively you should understand this as a requirement, because as the business keeps scaling big. So does the scale of complexity of devision making. In such situations we need a system by which we can segregate the business into smaller chunks to get guidance on decision making.
FAQ’s
Now, let me put up some common questions that might come in your mind regarding this topic.
- Define Departmental Accounting?
Definition of departmental account is an accounting process by which each separate division has a separate or combine allocated revenue and expenses allocation.
- What are the various departmental accounts format?
There are basically two formats, either it can be a columnar method where each department data is combined. While the other method is to create create different department profit and loss statements.
- What is department account meaning?
Department accounting system means that each department for example; sales, marketing, HR Or even by the division of business like clothes, accessories. The company basically creates calculates net profits, opening stock, overall performance , sale purchase each separately.
- Advantage of Department Account
There are various advantages to this method, but majorly it helps in analysing the efficiency, deciding the budget allocation and scaling decisions based on the performance.
- Importance of Departmental accounting?
As many business’s grow the capital allocation decision becomes more complex. Hence the management needs more guided precise information on such decisions.


