Let me put it this way, the trade settlement process is the following step after the stocks and bonds are purchased to move the securities from the seller to the buyer. So, from the context of Indian capital markets trade settlement usually happens in T+3 Days i.e 3 Days from the data of execution of the trade.
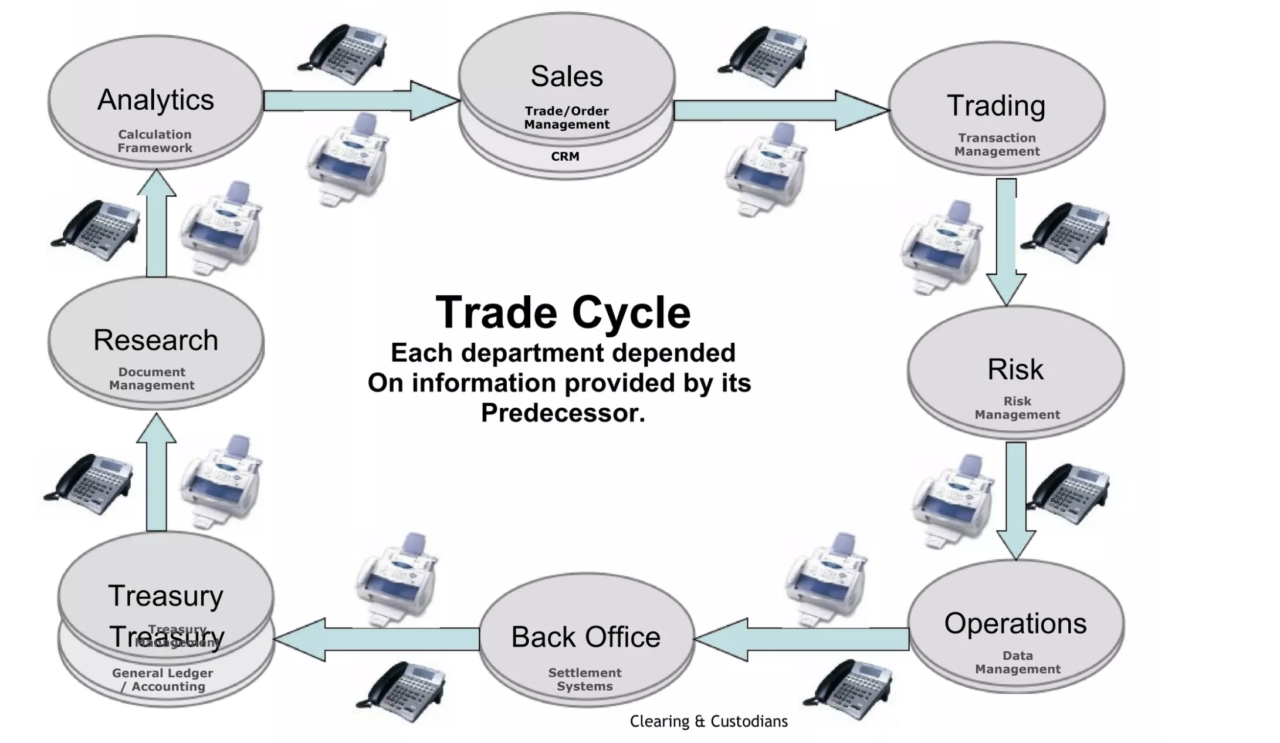
Trade settlement Process Overview
So, trade settlement process involves finalising a trade by exchanging assets and funds between parties. It ensures transaction completion according to terms. Now let me summarise the various kinds of settlement process’s examples;
- Stock Market Trade: After buying shares, the trade settles when the buyer’s account is debited, and the seller’s account is credited with the shares and funds.
- Foreign Exchange Trade: In forex, settlement occurs when currencies are exchanged between parties involved, usually two days after the trade.
- Commodity Trade: When a commodity trade is settled, the buyer receives the physical goods, and the seller receives the payment as per the trade agreement.
- Bond Trade: Settlement involves transferring the bond ownership to the buyer’s account and transferring funds to the seller based on the bond’s agreed price.
- Cryptocurrency Trade: Once a crypto trade is executed, settlement takes place when the agreed-upon amount of cryptocurrency is transferred from the seller’s wallet to the buyer’s wallet.
- Derivatives Trade: Settlement varies based on the derivative type. For futures, daily settlements occur, and for options, the settlement depends on the option’s exercise.
Trade Settlement Process Across Countries
Now, various countries and exchanges strive for different targets for settlement. Let me quickly take you through various trade settlement process across countries and exchanges.
Settlement process in NSE
The National Stock Exchange’s (NSE) rolling equity settlement cycle is as follows:
- Rolling Settlement Trading – T
- Clearing, which includes confirmation of custody and delivery generation – T+1
- Securities and Funds for Settlement Payments in and out – T+2
- Post Settlement Auction – T+2
- Auction Settlement – T+3
- Reporting for Bad Deliveries – T+4
- Rectified Bad Deliveries Pay-In-Pay-Out – T+6
- Bad Deliveries are being re-reported – T+8
- Re-Bad Deliveries are now closed – T+9
Settlement Process in BSE
Mentioned below are the steps of settlement by the Bombay Stock Exchange:
- The shares on the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) are all settled in T+2 days.
- T+2 days are also used to close government securities and fixed income instruments for individual investors.
- When you buy or sell securities, you pay in and out on the same day of the trade.
- After the BSE completes the pay-out of monies and securities, the client deposits the securities within one working day.
Settlement Guidelines in the U.S
Following are the guidelines for trade settlement process in the U.S markets according to various assets.
T-2 settlement dates for:
- Certificates of deposit (CDs): Same day
- Commercial paper: Same day
- U.S. equities: Two business days
- Corporate bonds: Two business days
- Municipal bonds: Two business days
- Government securities: Next business day
- Options: Next business day
- Spot foreign exchange (FX): Two business days
Trends in Settlement
There are various trends in trade settlement process going on across markets. While in the olden days settlement were static, and done on only specific days. Against which trade settlement process became a rolling affair, without any regards to a specific day. Now, the demands on the industry is towards faster trade settlement process. Let me summarise these trends below;
- Firstly the increase in trading volumes, which by the way puts direct pressure on manual settlement process and also leads to errors.
- Secondly, due to lower barriers to entry into the trade settlement process. Market participants are adding more value added services.
- Thirdly, reduction in margins and cost pressures due to the second effect.
- Fourthly, the customers are demanding faster execution and super fast information availability.
- Finally, the emergence of standards like FIX, ISO, ISIN which further complicates matter.
Categories of Risks in Trade Settlement Process
Now, let me briefly discuss on what critical risks exists in case of trade settlement process.
Principal Risk
Principal risk includes the risk of loosing the principal amount in the trade settlement process due to the counter party defaulting on the settlement.
Operation Risk
So, operation risk includes the risk to the capital due to inffeceient information systems or mis managed trading operations systems
Liquidity Risk
The risk of having low volumes and thus not able to execute a trade due to it.
Conclusion
Now, you might think that technology is the only challenge in this industry but for the trade settlement process to move towards T+1, is going to require more than that. So, briefly that means that there will be changes required in user skills, privacy and security, organisational structure and process design.