Last updated on December 15th, 2022 at 11:34 am
Commercial Banks in India: Explained with Indian Perspective

Author: Sarthak Bhalerao
Introduction
Banks play an essential part in the national development of the country. There have been a lot of ups and downs in our economy in recent times. The banking system forms the origin of the money management of any economy. Let’s look at what commercial banks are, the roles they play in the growth of the economy, and the structure and types of banks in India.
Table of Content
- What are commercial banks?
- Roles of commercial banks
- Structure of commercial banks
- Conclusion
What are commercial banks?
The term commercial bank refers to a financial entity that accepts deposits, offers checking accounts, makes various types of loans, and offers basic financial products and savings account to individuals and businesses. A commercial bank is where most people do their banking [1]. Banks make money by earning interests from mortgages, vehicle loans, business loans, and personal loans. The customer deposits provide banks with the capital, and they use this capital to give these loans.
Roles of commercial banks
Commercial banks in India are the backbone of all major economic activities in the country, whether it is for the citizens to keep their hard-earned money safely or get loans whenever they need funds for important things like a home, wedding, a car or for business. Banks help in accelerating the economic growth of a country in the following ways:
- Accelerating the rate of capital formation: Banks encourage the habit of thrift and mobilize the savings of people. These savings are allocated among the ultimate users of funds, i.e., investors for productive investment.
- Provision of finance and credit: Commercial banks are a very important source of finance and credit for trade and industry. The activities of commercial banks are not only confined to domestic trade and commerce but extend to foreign trade also.
- Develop Entrepreneurship: Banks promote entrepreneurship by underwriting the shares of new and existing companies. They also assist in promoting new ventures and financial activities.
- Promoting balanced regional development: Banks provide banking facilities to rural people by opening branches in the backwards areas. The funds collected in the developed regions may be channelized for developing these rural areas.
- Help to Consumers: Banks advance credit for the purchase of goods like vehicles, T.V., refrigerators, etc. which are out of reach for some consumers due to their limited paying capacity.
The commercial banks in India are divided into 4 sectors:
- Public Sector banks:
These are nationalized banks undertake by the government of India in one way or another. The government of India has a majority stake in these banks. Nationalized banks account for more than 75% of the overall business transactions that happen in the country [2]. As of today, there are 12 public sector banks all over India. They are as follows:
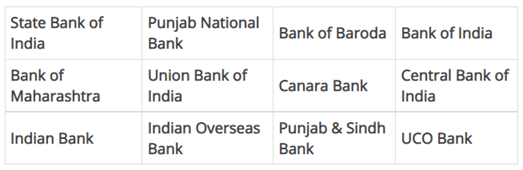
2.Private Sector Banks
Private Sector banks aim to provide high quality and privileged services to their customers. These banks are privately owned and are operated by High-Net-worth Individuals (HNI) and business organizations [3]. These banks majorly work on the lines of profit-making by keeping deposits providing loans and other products related to financial activities.
The major private sector banks in the country are:
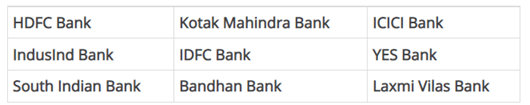
3.Foreign Banks:
Foreign banks are a kind of International Bank that are obligated to follow the regulations of the home country as well as the host country. They have their headquarters outside the country, but they run their offices as a private entity at any other location outside the country. Foreign banks have a presence in India either as a representative office or as a branch. There are a total of 45 international banks in India [4]. Some of them are as follows:
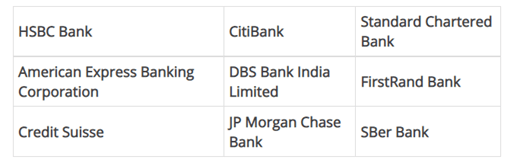
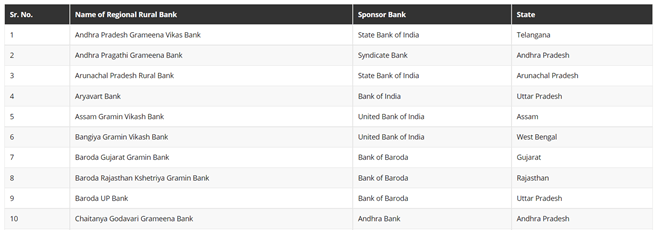
4.Regional Rural Banks:
The main objective behind the formation of such banks is to provide credit support to economically weaker sections of the society like labourer’s, farmers, rural traders, and small business owners. Most of these banks are regional as the name suggests, which means these banks operate in particular regions and might have branches in the metropolitans as well. These rural banks work on specific lines and serve major functions like providing financial credit support to rural and semi-urban areas, provide support for government schemes, etc. They also provide card and locker facilities to their customers. A few of these banks are [5] as follows:
Conclusion:
Commercial banks play an important role in fulfilling the short-term and medium-term credit requirements of the individuals who help in the economy. However, they do not provide long-term credit for over 15 years or more, so that liquidity of assets can easily be maintained. The funds parked at the commercial banks belong to the general public and are withdrawn at a short notice. Therefore, commercial banks prefer to provide credit for a short period of time backed by tangible and easily marketable securities.

