In today’s dynamic business world, every financial decision big or small has a ripple effect. Whether it’s funding a new project, managing day-to-day cash flows, or planning for long-term growth, corporate finance lies at the heart of it all. It’s the engine that keeps businesses running efficiently, strategically, and profitably. But why exactly is corporate finance so crucial and how does it impact companies, investors, and even you as a consumer or job seeker?

This article explores the real-world significance of corporate finance, from capital allocation and risk management to value creation and strategic planning. Whether you’re a student, a professional, or a curious reader, understanding corporate finance isn’t just useful it’s essential for you to understand finance and its dynamics.
What Is Corporate Finance?
Corporate finance is the area of finance that focuses on how companies raise funds, invest money, and manage financial resources to maximize business value. It helps firms make smart financial decisions that support growth, profitability, and long-term stability.
Key Areas of Corporate Finance
Capital Budgeting: Deciding which projects or investments a company should undertake (e.g., NPV, IRR analysis).
Capital Structure: Choosing the right mix of debt and equity to finance operations at optimal cost.
Working Capital Management: Managing short-term assets and liabilities to ensure liquidity and smooth operations.
Dividend Policy: Deciding how much profit to distribute to shareholders versus reinvest in the business.
Why Is Corporate Finance Important?
Corporate finance is a big deal because it helps companies make good money choices that boost their worth and lower their risks. It makes sure that the money they have is spent wisely to make steady profits.
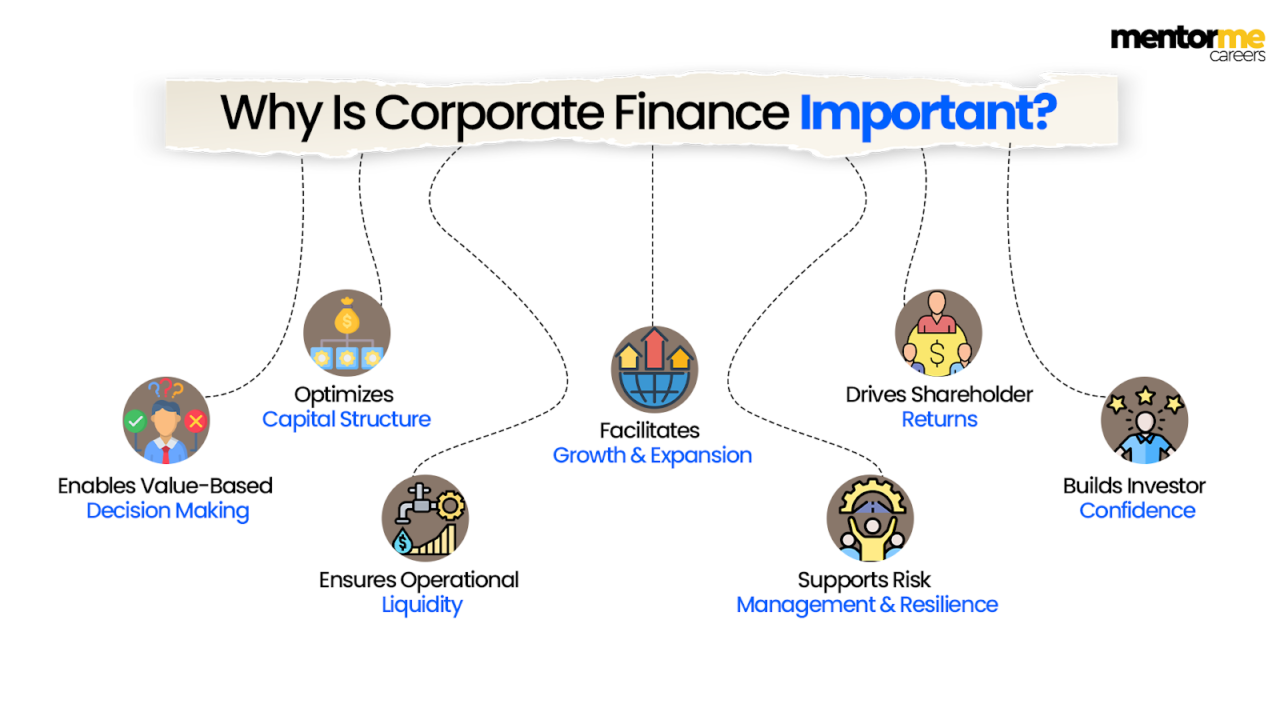
Enables Value-Based Decision Making
Corporate finance is all about making a company as valuable as possible.
That means leaders look at financial data to figure out which projects are worth putting money into, which ones to skip, and how to best use what they have to bring in the most cash.
Optimizes Capital Structure
Helps companies figure out the best way to get money, whether that’s through borrowing or selling off parts of the company.
Getting this funding mix right can lower the cost of getting money, boost profits, and keep financial risks in check.
Ensures Operational Liquidity
Through smart management of day-to-day cash, corporate finance makes sure a company always has enough money to cover things like paying employees, suppliers, and other immediate bills.
Facilitates Growth & Expansion
When a company wants to do things like roll out new products, expand into new areas, or buy other businesses, corporate finance looks at how much money is needed and what the expected returns are to make sure the growth can last.
Supports Risk Management
By taking a close look at how much debt a company has, how much cash it’s generating, and its financial risks, corporate finance helps businesses get ready for tough economic times, changes in interest rates, and shifts in the market.
The choices a company makes about paying out dividends, reinvesting profits, or buying back its own stock really affect how much shareholders are worth, so corporate finance is key to keeping investors happy.
Builds Investor Confidence
When companies are upfront about their finances, plan well, and show good results, it builds a lot of confidence with investors, people who lend them money, and everyone else involved.
Core Functions of Corporate Finance
Corporate finance covers key areas. These include investment decisions (capital budgeting). It also involves financing decisions (capital structure). Operational efficiency (working capital) is another focus. Corporate finance balances shareholder returns (dividend policy). It also considers risk control (risk management). The goal of these functions is to maximize shareholder wealth.
| Corporate Finance Function | What It Involves | Key Tools / Metrics Used | Objective |
| Capital Budgeting | Evaluating and selecting long-term investment projects | NPV, IRR, Payback Period, Profitability Index | Maximize firm value by investing in profitable projects |
| Capital Structure Management | Deciding the optimal mix of debt and equity financing | Debt-Equity Ratio, WACC, Cost of Debt, Cost of Equity | Minimize cost of capital and optimize risk–return |
| Working Capital Management | Managing short-term assets and liabilities | Current Ratio, Quick Ratio, Cash Conversion Cycle (CCC) | Ensure liquidity and smooth day-to-day operations |
| Dividend Policy | Deciding how much profit to distribute vs retain | Free Cash Flow (FCF), Dividend Payout Ratio, Retention Ratio | Balance shareholder returns with future growth |
| Risk Management | Identifying and mitigating financial risks | Hedging, Derivatives, Value at Risk (VaR), Sensitivity Analysis | Protect cash flows and firm value from uncertainties |
Key Corporate Finance Metrics & Formulas
NPV & IRR – Used for investment and project evaluation
WACC – Used as discount rate in valuation models
EVA – Used for value creation measurement
FCF – Used in DCF valuation and dividend decisions
| Metric | Formula | What It Measures | Where / When It Is Used |
| Net Present Value (NPV) | NPV = Σ [cashflow/(1+r)^t] − Initial Investment | Value created by a project after accounting for time value of money | Capital budgeting decisions; project acceptance if NPV > 0 |
| Internal Rate of Return (IRR) | IRR = Discount rate where NPV = 0 | Expected annual return generated by a project | Comparing mutually exclusive projects; investment appraisal |
| Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC) | WACC = ( \frac{E}{V} )×Ke + ( \frac{D}{V} )×Kd×(1−T) | Firm’s average cost of financing | Discount rate in DCF valuation; capital structure decisions |
| Economic Value Added (EVA) | EVA = NOPAT − (WACC × Capital Employed) | True economic profit generated above cost of capital | Performance measurement; value-based management |
| Free Cash Flow (FCF) | FCF = Operating Cash Flow − CapEx | Cash available for shareholders and debt holders | Dividend policy; valuation; debt repayment analysis |
| Return on Capital Employed (ROCE) | ROCE = EBIT ÷ Capital Employed | Efficiency of capital utilization | Comparing operating performance across firms |
| Debt-Equity Ratio | Debt ÷ Equity | Financial leverage level | Capital structure analysis |
| Interest Coverage Ratio | EBIT ÷ Interest Expense | Ability to service debt | Credit risk analysis; lender assessment |
Corporate Finance in a Modern Business Context
Corporate finance is all about more than just making money, it’s about growing steadily, finding good ways to get funds, and making choices based on solid information. Today’s companies use it to weigh up how much they can earn against being responsible, able to bounce back from challenges, and coming up with new ideas.
Role in ESG & Sustainable Financing
Now, corporate finance also includes looking at Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) stuff when deciding where to put money. Businesses are getting cash through things like green bonds, loans tied to sustainability, and funds focused on making a positive impact. This means their money plans line up with fighting climate change, being ethical, and helping society. Doing this helps them create value over time, lowers the chance of running into trouble with rules, and makes them more appealing to investors from all over.
FinTech, AI & Capital Sourcing
Technology has totally changed how corporate finance works. FinTech tools make it easier to raise money, manage cash, and handle payments. Plus, AI and data analysis are getting better at predicting things, figuring out risks, and deciding where to invest money. Companies can now get funding from places like venture debt, private lenders, or crowdfunding much more quickly and easily than going the old-fashioned route.
India & Emerging-Market Advantage
In India and other developing countries, corporate finance is super important for helping businesses grow, dealing with unpredictable markets, and keeping up with changing rules. Being able to tap into local money markets, get government help, and use digital financial systems gives companies a real advantage when they want to expand and compete on a global scale.
Real-World Applications for Students & Professionals
1. How Corporate Finance Is Used: Startups vs Large Corporations
In Startups
Focus is on cash burn, runway, unit economics, and fundraising valuation
Capital budgeting is used to decide product launches, marketing spend, and expansion
Capital structure decisions revolve around equity dilution vs venture debt
Working capital management is critical due to limited cash buffers
In Large Corporations
Focus is on large-scale capital budgeting (plants, acquisitions, global expansion)
WACC is used extensively for DCF valuation and M&A decisions
Dividend policy and share buybacks become key shareholder-return tools
Risk management involves hedging FX, interest rate, and commodity risks
2. What Recruiters Look For in Corporate Finance Roles
Recruiters typically assess three things: skills, tools, and financial thinking.
Core Skills Recruiters Expect
Financial statement analysis
Capital budgeting (NPV, IRR)
Valuation basics (DCF, comparables)
Risk analysis and scenario thinking
Tools Recruiters Value
1.Advanced Excel (financial models, sensitivity tables)
2.Power BI / Tableau for reporting and dashboards
3.Exposure to ERP systems (SAP, Oracle – bonus)
4.Financial modelling templates (3-statement models)
Metrics Recruiters Expect You to Understand
NPV, IRR, WACC
Free Cash Flow (FCF)
ROCE, ROE
Debt-Equity and Interest Coverage
Cash Conversion Cycle (CCC)
3. How Students Can Apply Corporate Finance Knowledge Practically
Through Internships
1.Apply ratio analysis on real company financials
2.Assist in budgeting, MIS reporting, or valuation support
3.Work on live Excel models instead of textbook problems
By Learning the Right Tools
1.Build 3-statement financial models in Excel
2.Create dashboards using Power BI or Tableau
3.Practice valuation using annual reports of listed companies
4.Simulate investment decisions using case studies
Through Projects & Certifications
1.Equity valuation projects
2.Startup financial projections
3.CFA-aligned coursework or financial modelling programs
4.Case competitions and live simulations
Conclusion
Corporate finance isn’t just a buzzword thrown around in boardrooms it’s a foundational pillar of every successful business. From guiding investment decisions to maximizing shareholder value and managing risks, its influence is everywhere. Whether you’re eyeing a career in finance, pursuing a BBA, or simply trying to make sense of how companies grow and thrive, understanding corporate finance will sharpen your perspective and open up countless opportunities.
Ready to dive deeper into the world of corporate finance?
Book your free 1-on-1 counselling session with our career experts at Mentor Me Careers. We’ll walk you through career paths, certifications like CFA, job trends, and how you can build your foundation in finance at no cost.
Start your journey into corporate finance today – schedule your free counselling now!
FAQ
Corporate finance is important because it helps businesses maximize value, manage money efficiently, and make smart long-term decisions about investments, funding, and growth.
Corporate finance aids decision-making by using data, financial analysis, and valuation techniques to choose the best options for investing, financing, budgeting, and risk management.
Common corporate finance metrics include NPV, IRR, ROI, cost of capital (WACC), cash flow, debt-equity ratio, and profitability ratios, which help evaluate performance and decisions.
Accounting records past financial data, while corporate finance focuses on future decisions like investments, funding strategy, and value creation using financial analysis.
Yes. Even small businesses can apply corporate finance principles to manage cash flow, control costs, plan growth, raise funds, and reduce financial risk effectively.
Related Articles
- Scope of corporate finance
- CFA curriculum level 1 updates
- which is better CFA or financial modelling
- top finance courses in India
- CFA exam pattern



